Therapeutic dentistry
Doctors of ‘Aregak’ dental clinic, in number of others, diagnose and treat even the most complicated and rare cases met in the practice. The key to success is the complex approach, great experience, perfect scientific preparedness and skills of the specialists.
Therapeutic dentistry has the biggest demand, that’s why the therapist-dentist takes the first place in the complex treatment of oral problems of the patient. The therapeutic treatment is the basis without which it’s impossible to provide the oral health state and the quality of further medical procedures.
In the therapeutic compartment of ‘Aregak’ dental clinic services provided include:
- Caries treatment by stopping or placing ceramic inlays according to indications.
- Caries complications treatment (pulpitis, periodontitis)
- Cosmetic restoration with composite materials, ceramic veneers to correct the form of frontal teeth and improve the color
- Tooth whitening,
- Periodontological treatment,
- Dispenser control of the patient-free preventive examination twice a year
All medical procedures are performed according to medical indications, the newest methods and materials are used that provide perfect result.
Caries
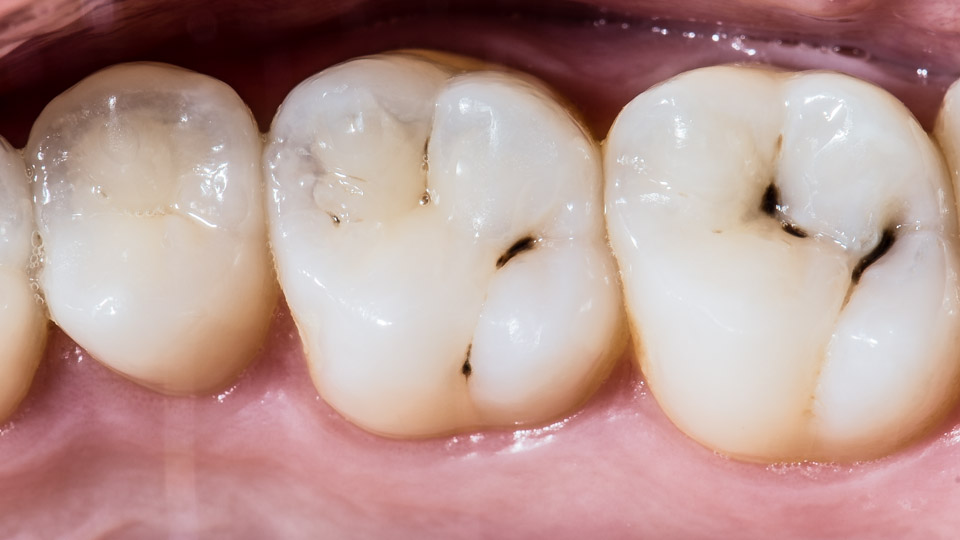
Caries is a rather widespread dental disease. Today nearly everybody has problems with caries and its complications. As it has been mentioned, caries is necrosis of hard tissue of the teeth. The worst thing is that the process irreversible. In other words it may be prevented but it is not possible to restore the lost tooth tissues. So it would be better not to wait until the caries is developed, but to prevent it. The caries is prevented productively to children, especially the pressurization of dental fissures. The external factors (food, oral hygiene), heredity, as well as the total health state of the organism (immune, digestive systems) also have an important role in the development of the caries. Besides poor cleaning another cause of dental caries may be improper feeding (insufficiency of carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, fluorine), the abuse of candy, as well as the stress.If the caries is developed anyway, it is important to turn to dentist possibly early to start the treatment. To treat the deep caries is difficult and lasts comparatively long. This can cause serious complications.
The term caries means 'rotting'. The caries is developed gradually: first a pigmental stain appeares on the tooth surface (white, then yellow) that turns brown soon. Then the enamel is decayed and then it comes the dentine's turn. The hollow appeared first on the enamel, then on dentine gradually enlargenes and deepens. The food remnants gathered in the cavity and create a nutrisious environment for the microbes.
If no medical procedures are performed the pathological process is developed and the tooth is decayed totaly and complications rise. To the number of main complications belong the pulpitis and periodontitis.
The dentists differenciate between two stages of caries:
-early, when the caries stain appeares (white and pigmental).
-late, when a hollow appeares in the hard tissue (superficial, middle and deep caries). Caries becomes the reason of anatomic, functional and aesthetic defects of the tooth.
The soft deposit forms immediately during the eating process. It contains small remnants of food and generally consists of carbohydrate. If the tooth is not cleaned, the soft deposit hardens and sticks to the tooth firmly. And the microbes ‘inhabiting’ there transform the carbohydrates into acids. The tooth enamel softens under the influence of the acids.
This is the first stage of the development of the dental caries-the caries stain. In this stage it is still possible to stop the morbid process.
In the second stage of caries the process is aggravated and reaches to dentine-to the main tissue immediately under the enamel. The dentine is less stabile towards the caries than the enamel and thus the tooth destruction becomes more rapid and severe.
That is the middle stage of caries. If in this stage the caries is not treated the destruction of dentine leads to a hollowing.
That is already the deep caries.
To recognize the caries is rather easy, the symptoms are:
-on the teeth surface (especially on the chewing surface) dark pigments appear
-the surface of the tooth roughens
-there is a feeling of light pain while eating, the tooth is supersensible towards sweet and acid, hot and cold
-there may be fetid odor in the mouth
-with toothpick or tongue it is possible to grope for the hollow in the tooth
The caries may deeply injure the tooth and reach to the most delicate part of the tooth-pulp, where the nerves and vessels are. The lesion to this degree may be accompanied by strong pain and is called pulpit.
The caries is developed as a result of vital activities of microbes in the dental deposite. The dental deposit in its turn is developed from cooked food, which contains great number of carbonhydrates. So, a soft dental deposit is gathered on the surface of the enamel and in those parts of teeth from where it is not cleaned while chewing, it clings frimly and becomes a 'place' for the accumulation of microbes. If the dental deposit is not cleaned on time, the microbes multiply quickly. The more the amount of microbes rises, the more they produce acids which clean calcium and flourine from the surface of enamel. The enamel softens gradually and the microbs penetrate deeper in the tooth damaging it.
To some perople the resistance is weak to other it is rather high. The stability of teeth towards the caries depends on the protective system of the organism, concomitent diseases. The factor of heridety is also very important. It is determined that to the people with low imune system caries develops more actively. Important roles play the composition and the properties of saliva. To the people having dental caries the saliva is more viscous and in its composition the ratio of minerals is changed.
The external factors (food, oral hygiene), heredity, as well as the total health state of the organism (immune, digestive systems) also have an important role in the development of the caries. Besides poor cleaning another cause of dental caries may be improper feeding (insufficiency of carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, fluorine), the abuse of candy, as well as the stress.
If the caries is developed anyway, it is important to turn to dentist possibly early to start the treatment. To treat the deep caries is difficult and lasts comparatively long. This can cause serious complications.
The dentists in the ‘Aregak’ dental clinic treat patients of any age with the newest and painless methods, with new materials and with anesthetics of the last generation. Besides, the patients of the clinic are explained the ways of caries prevention, the correct oral hygiene, the right choice of hygienic means that would help to prevent caries.
Today the caries treatment is not painful at all and is done with anesthesia. The destructed dental tissues are removed and then the cavity is filled with newest inlay materials. It is necessary to turn to the dentist in case of first symptoms of dental caries as the later the treatment is, the greater the surface of the tissue destruction is.
It is recommended to do a regular professional oral cleaning which would allow cleaning efficiently dental deposits and dental plaque from the difficult-to-reach zones which will prevent the caries development.
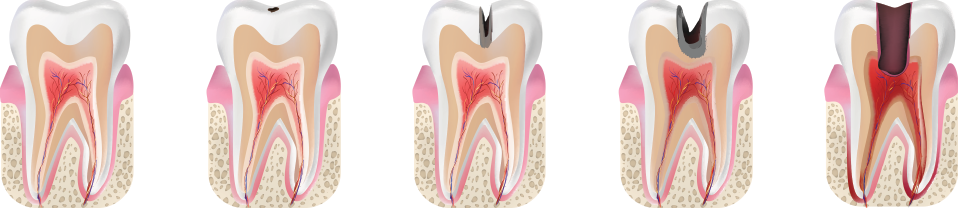
Superficial caries: the dental enamel is damaged or not a big dental inlay has fallen or there is a small hollow in the tooth. The tooth treatment supposes elimination of enamel defect and restoration of its anatomical form, color and chewing function.
Middle caries: in this case the ½ of hard tissue is damaged (enamel and dentine). It might be detected after the dental inlay has fallen or when the doctor is handling the tooth and a mid-depth caries zone is uncovered behind a small hollow. The tooth treatment supposes the elimination of enamel defect and the restoration of its anatomical form, color and chewing function.
Deep caries: more than the ½ of the hard tissue of the tooth is damaged, but the nerve is not infected. The treatment is done by elimination of the defect on enamel and dentine with the help of dental inlays (dentine forming medicine is used), the form of tooth, color and the chewing function are restored.
If during caries treatment considerable destruction of inner tissues of tooth is detected and the restoration is not possible, then there rises need for prosthetics by placing an inlay or crown, or (exceptional cases) tooth extraction.
As far as the tooth tissues do not regenerate, the caries treatment is realized by extraction of the injured tissues; the generated defect is eliminated by special filling or by placing a so called ceramic inlay. The goal of all artificial materials is not only to hide the defect but also to replace the lost volume of the tissue, as well as to restore the anatomic form of the tooth for full restoration of the functional problem. If the defect of the tissue is rather remarkable then it is advised not to use filling, but to place a ceramic inlay for it is more reliable and firm because of equal distribution of chewing load.
Secondary caries means repetition of caries lesion after a therapeutic treatment. The reasons for it may be different. If the infected tissues are not removed completely then the process may develop under the inlay. The wrong usage of this or that material, as well as not keeping the rules while placing the inlay may cause the development of secondary caries. Another reason may be the usage of the material of low quality that can’t sustain the pressurization and secondary caries is developed. The third reason is the insufficient personal oral hygiene that may provoke a secondary caries of healthy tooth tissues.
Many people think that in the teeth undergone depulpation can’t develop caries and they get surprised knowing that especially in those teeth caries is developed. As far as caries (primary and secondary) is a necrotic process that decays the hard tissue of the tooth, the presence of nerve in that process does not play any role.
Caries is a rather widespread dental disease. Today nearly everybody has problems with caries and its complications. As it has been mentioned, caries is necrosis of hard tissue of the teeth. The worst thing is that the process irreversible. In other words it may be prevented but it is not possible to restore the lost tooth tissues. So it would be better not to wait until the caries is developed, but to prevent it. The caries is prevented productively to children, especially the pressurization of dental fissures.
To prevent caries it is important
- to feed correctly. Fresh fruits and vegetables should dominate in the food. The confectionery and sweets should be limited.
- To clean teeth in the morning and evening not less than 2-3 minutes with correctly chosen toothpaste and toothbrush.
- To perform professional oral cleaning regularly
- To visit the dentist twice a year for preventive dental examination.
There exist preventive measures that should be started yet in the intrauterine development period of the fetus, as far as in that period the basis of the teeth formation is put. The lifestyle of the future mother, her detrimental habits immediately affect the teeth quality of her child.
After kid’s birth it is very important his nutrition-breast feeding, giving vitamins and minerals sufficiently and on time (one should be careful not to exceed the quantity), the elimination of bad habits of the kid (to suck the finger, mouth breading, biting pens and pencils, etc.). Pulling all this together we may say that the first point of caries prevention should be explanations given to future parents about the reasons of caries development and its dangerous consequences.
The second point is already the private oral hygiene that should be kept immediately after the first milk teeth appeared. Naturally, at the beginning it does mother and later she teaches the kid to do that on his own, of course, controlling his actions.
Cleaning the dental deposit mechanically we exclude the risk of caries generation. But if there is already a process then only teeth cleaning would not help.
That’s why the third point of caries prevention is the professional oral hygiene and the dentist’s preventive examination.
Pulpitis
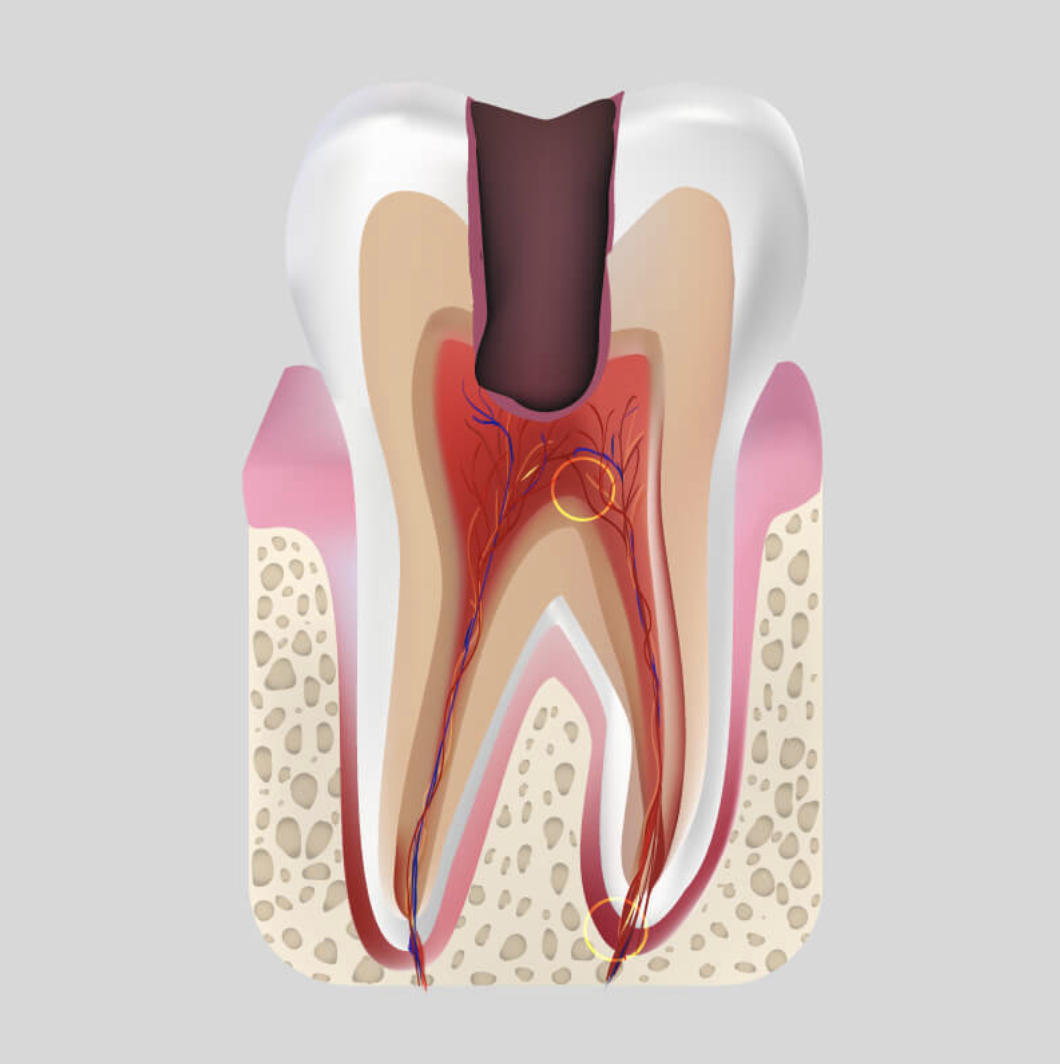
Inside the tooth its soft tissue (the pulp) is placed where the blood vessels, lymphatic nodes and the nerves are.
The pulpitis is the inflammation of the soft tissue (inflammation of nerve), that is generated because of the pathogenic microbes penetrated there.
The microbes in the mouth cavity produce acids from sweet food that decays the enamel of the tooth generating caries. In case of complicated caries the microorganisms penetrate inside the tooth which causes the pulp inflammation. Pain arises that is transformed to the triple nerve because of which the pain echoes in the temples, nape, ears and throughout whole face. The microbes may also penetrate inside the tooth in case of lesion of periodontium.
The inflammation of the nerve is characterized by strong pain, the tooth becomes sensitive towards the temperature changes, the pain usually strengthens at night.
Often the pulpitis is one of the complications of caries when the tooth is destructed so that the infection reaches to the tooth root and affects the nerve. Sometimes the pulpitis may arise because of doctor’s wrong actions (low-quality stopping, surgery of periodontium, effect of chemical materials). Pulpitis may also be the result of tooth trauma-tooth fracture, crown fissure.
As it has already been mentioned, pulpitis is characterized by sharp pain that strengthens especially at night echoing in the ears, temples, or pharynx. In the first stage the pain rarely raises and calms down quickly, but with development of pulpitis the pain raises more and more frequently. It becomes stronger and pulsation takes place when pulpitis passes to its purulent stage, sometimes even loss of conscience might happen.
In case of diffusive pulpitis the pain might be expressed not only in the tooth but also it may spread over the jaw and the part of the head where infected tooth is. Because of the pain is spread sometimes it becomes difficult for the patient to point out the spring of the pain. But it can be detected independently if the tooth reacts towards hot, cold and other provocative. It is typical that during pulpitis the pain doesn’t calm down after elimination of provocative. No analgesic or folk method helps as far as the treatment of pulpitis is done in the dental clinic only.
The symptoms of pulpitis are similar to the symptoms of other inflammatory lesions (especially inflammation of triple nerve), that’s why only doctor can put the right diagnosis.
Pulpitis may proceed in exacerbated and chronic stages. We have already described the symptoms of exacerbated pulpitis. The symptoms of chronic pulpitis are not expressed so vividly. In this case sensitivity towards hot and cold raises, the patient complains from the fetid odor in the mouth and while visiting the dentist enlargement of pulp is diagnosed. The danger in case of chronic pulpitis is that it can change into periodontitis. In case of chronic pulpitis also exacerbations may occur; in this case paroxysmal toothache arises that strengthens effected by thermal provocatives.
But in case of chronic gangrenous pulpitis as well as in case of exacerbated purulent pulpitis, the tooth reacts only to the hot; the cold visa versa weakens the pain.
If pulpitis is not treated then in the bone tissue periodontitis may be developed or purulent periodontitis that may transform to gumboil, abscess, phlegmon, even it may end with fatal consequences.
The treatment of pulpitis which is realized in early stage allows keeping the nerve that is needed for nutrition of the tooth and its normal vital functioning; for that reason it is necessary to turn to dentist immediately. In this case the treatment of pulpitis includes effecting on the infected pulp with special medicine containing calcium (biological method).
During the treatment of pulpitis anesthesia is done beforehand. Unfortunately, many patients turn to dentist rather late when the analgetics do not provide necessary effect; a morbid process has developed and has passed from exacerbated stage to chronic one.
When the patient turns to doctor late the later has to undertake more radical measures. In case of pulpitis in the stage of strong inflammation it is the extraction of nerve that is followed by endodontic treatment.
The serous pulpitis needs appropriate treatment- placing a calcium containing material under the dental inlay, antibiotic therapy and so on. Partial extraction of pulp is also possible. In case of strong purulent and chronic pulpitis depulpation is done and in the dental canal filling is done.
To prevent pulpitis it is necessary
– to clean teeth always and regularly,
– to limit sweets,
– to visit dentist once in half year.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is the inflammation of periodontium. In this case the inflammatory lesion is developed in the zone of periodontal tissue of the dental root. Depending on the degree of pathological changes acute and chronic periodontitis are distinguished; acute-serous, purulent, chronic-fibrosis, granuloma and cyst, exacerbation of chronic periodontitis.
Periodontitis is the most dangerous complication of caries lesion.
In case of chronic periodontitis the inflammation is developed very slowly, sometimes without pain, and as a rule is not aggravated. In case of chronic periodontitis everything is expressed weaker, but may be accompanied by swell, reddening of gingiva, high temperature which already is typical to acute periodontitis. The chronic periodontitis is especially dangerous because the microbes breeding freely around the tooth extract toxics that intoxicate the human organism for long years becoming reason of heart, kidney, articulation diseases.
The main cause of periodontitis is infection that may penetrate to periodontal tissue through caries cavity, to root canal through gingival pockets, or with blood (hematogenic way).
Another reason for periodontitis may be the trauma or provocative effect of medicine. In this case the periodontitis is called traumatic or toxic.
Because of provocative effects of infections, toxics, medical preparations, or traumas inflammation is developed in the periodontium. It causes tissue swelling and as the flow of inflamed liquid becomes difficult in periodontium, the lesion is accompanied by acute pain.
The pain gradually strengthens. As a result the liquid finds a way either through the root canal or gingival pocket or mandibular periosteum and the acute development calms down. In some cases the inflammation may not acquire acute development and the lesion becomes chronic.
Periodontitis is a caries complication, when the infection passes from carious cavity to pulp from where it penetrates to periodontium and generates the disease. The tooth starts to move and aches even in case of a light touch. The body temperature rises. The periodontitis may last without pain; in this case resorption of the bone around the root takes place, granuloma which later may change into cyst-granuloma and cyst, which demand more serious treatment in order not only for keeping tooth but also for preventing intoxication of the organism. If the patient has more than one tooth infected with periodontitis then there is great possibility of diseases of kidneys, heart, joints.
The periodontitis may also be developed because of the low quality treatment of root canals. Following teeth are often sentenced to be extracted if the roots are not possible to treat. The canals are elaborated with special needles, antiseptic materials, ultrasound. Often several visits to clinic are needed in this case. Usually the ‘salvation’ of tooth is important for later prosthetics.
Periodontitis, as it has already been mentioned, is expressed by sharp pain around the tooth that strengthens even from a light touch. The lip, cheek, gingiva swell and there is fetid odor in the mouth, sometimes there is fistula on the gingiva.
Periodontitis may be infection or not infection.
The main roles in the development process of periodontitis acquire the microorganisms and the poison extracted by them. They penetrate to periodontium through root canal, periodontal pocket or in hematogenic way generating dangerous inflammation.
The microorganisms and the extracted poison.
It is developed because of the following reasones:
1. Trauma
а. Immediately, acute (knock, trauma while filling the canals, trauma of periodontium while treating pulpitis, cracking nuts with teeth or while biting a bone)
b. chronic micro-trauma (biting off pipe, brass instruments, pens, pencils, inlay put highly and so on)
2. the effect of medicine
When a strong effecting medicine is reached to periodontium while enlargement of the root canals, disinfecting them, etc.
The treatment of periodontitis is multi-stage. The methods are chosen according to a concrete case. Special gels are used that help the vesicle, granulоma resorbtion and restoration of bone tissue.
Sulfanilamides preparations are prescribed that have antibiotic effect, as well as allergic preparations to calm down the pain. But these methods are not comparable for the main treatment is done by the dentist.
During the first visit the following steps are done:
1. diagnostic X-ray imaging
2. anesthesia
3. caries treatment
4. extraction of necrotic pulp from the crown, root canals cleaning with antiseptic medicine.
5. measurement of the length of root canales
6. mechanical enlargement of those canals (simultaneously performing ablution of canals with antiseptic medicine)
7. injection of antiseptic medicine in the root canal until the next visit.
8. temporary stopping
During the next visit:
1. extraction of temporary inlay
2. canal cleaning with antiseptics
3. quality stopping with gutta-percha.
In some cases of acute or chronic periodontitis when the therapeutic methods of treatment are insufficient, tooth extraction is necessary to do. The extraction is indicated to prevent the spreading of inflammatory lesion in the bone and soft tissues. Sometimes the quick extraction needs only several hours. Sometimes in case of chronic periodontitis the tooth is so decayed that it becomes impossible to restore its anatomic form, or use the root as a basis of pin.
Meanwhile the tooth extraction is indicated in that case when there is a complicated periodontitis and in order the inflammatory liquid would come out a necessity to snick the periodontium in the upper part of dental root in between the gingiva. This interference is indicated in case of swell of the soft tissue.
The combination of the surgical interference and medical treatment allows eliminating quickly the inflammatory lesion.
Endodontics
Endodontics is a root canal therapy, the main goal of which is tooth preservation. As it is said one can always put prosthesis, but one should try to keep his own teeth as much as possible.
During endodontic therapy the usage of modern technologies- surgical microscope, ultrasound, tooth of nickel-titanium, apex-locator and so on, give the dentist more opportunities to keep the tooth and reach positive results in such clinical cases when it was impossible several years ago.
Necessity for such treatment raises in case of development of caries complications (pulpit, periodontitis), tooth fissures, sometimes in the preparatory stage of placing prosthesis. Endodontics is indicated also in case of double treatment when at first time the tooth canales were wrongly treated.
The aim of practical endodontics is to prevent the development or eliminate already existing inflammatory centers of periodontium that are one of the main reasons of loosing teeth. To reach to that goal it is possible only by antibacterial treatment and hermetic closing of root canals which is accompanied with hermetic restoration of dental crown. To realize practical endodontics it is necessary to put the right diagnosis and to work out the precise planning of the treatment.
The diagnosis, as it is known, includes
• collection of anamnesis of illness and lifestyle to find out the allergic state, functional state of inner organ-systems;
• the objective examination of maxillofacial zone of the patient to detect asymmetry, swell, fistula;
• palpation of lymphatic nodes, temporomandibular joint.
The examination of mouth cavity is directed to turn out the state of oral hygiene, mucosa, periodontium, fistulas, the existence of inflammations. Summing up the data of clinic-laboratorial examinations the diagnosis and treatment planning is done.
The treatment of tooth canal may be done in several stages. As a rule a local anesthesia is done. The choice and dose of anesthetic drug depends on the age, weight, duration of dental intervention and allergic card of the patient. The tooth is isolated by special latex texture (rubber-dam) and then the doctor starts to clean the tooth canals with special equipments, tools and medicine under the control of X-ray and apex-locator.
The treatment of tooth canal may be done in several stages. As a rule a local anesthesia is done. The choice and dose of anesthetic drug depends on the age, weight, duration of dental intervention and allergic card of the patient. The tooth is isolated by special latex texture (rubber-dam) and then the doctor starts to clean the tooth canals with special equipments, tools and medicine under the control of X-ray and apex-locator.The usage of rubber-dam during the endodontic treatment is desirable as far as it provides aseptic work conditions, prevents the infection of tooth cavity with microorganisms by saliva or air being respired; prevents the patient from swallowing accidentally small endodontic instruments. With rubber-dam the time is saved, it becomes easier to make a hollow on the tooth; the quality of treatment remarkably improves.
The endodontic treatment starts with making a hollow on the tooth. There may raise difficulty in tool elaboration of root canal if the cavity is not opened sufficiently or the direct approach to the root canal is impossible. While opening the hollow one must always remember the anatomic structure of the tooth. The correct detection of the length of root canal of the tooth is one of the most important stages of the treatment. The enhanced apex-locators enable to detect correctly the length of the canal; the X-ray imaging also comes to help and gives not only insight about the length of the canal, but also about its curvature or the existence of other canals. In some cases the root canals are filled in the first stage, but often medical preparations are required. In this case the final filling and treatment are done during the next stages. During the period between the stages either a temporal crown is placed or temporary inlay to protect reliably the root canals of the tooth from penetration of microorganisms.
The professional tooth stopping is very important. The classical way of stopping is filling the canals with special latex-like material which is called gutta-percha. There are several ways of stopping with this material: thermo-fill, lateral condensation and thermo-gutta-percha.
Thermo-fill and lateral condensation are used to work with available canals. The thermo-gutta-percha (movable hot mass) fills both the main and the micro canals where the tools do not reach. That material shrinks as it cools and covers all micro-cracks and holes so that the microorganisms cannot breed there.
In a word we can say that thermo-gutta-percha is the most modern and developed method. This method gives the opportunity to fill even the root canals having complex anatomic structure which are nearly impossible to fill another way.
In our practice the method of vertical condensation provides higher clinical reliability giving opportunity to fill the root canals of tooth equally that is being checked by X-ray imaging. In this case such complications as re-stopping or under-stopping are practically excluded. This method is used for most clinical case of teeth treatment, as far as it gives the opportunity to provide long-term treatment. Our clinical experience has shown that the vertical condensation method of tooth treatment with thermoplastic gutta-percha is the most productive and long-term method.
The treatment of root canals of tooth may be controlled and the final result may be estimated by X-ray imaging which is done 12-18 months later and give the opportunity to detect the existence or absence of inflammatory developments in the upper part of the tooth. But as a rule the clinical signs of the inflammation (pain, swell, etc.) are eliminated 1-2 weeks later after the beginning of the therapy and the restoration of the crown may be done several days after the treatment of the root canals.
In the practice of ‘Aregak’ clinic two methods of endodontic therapy are used as far as they fit all the standards of high-quality filling of root canals. With all this the patients always have maximal choice in the treatment methods as that allows both the doctor and the patient to choose the most suitable method for each concrete case to reach the main goal-to keep health.
Oral Mucosa diseases
The mucosa of mouth cavity is always affected by different provocatives-chemical, mechanical, thermal, many microbes and toxic materials. Besides the mouth cavity is a sensitive indicator that shows the functions of internal organs and signals operatively when something is wrong with one of the organs. If one of the defensive factors has weakened, there arises risk of development of inflammatory lesion of mucosa. The most widespread types are stomatitis and glossitis.
- The trauma of oral tissues (chemical, thermal, etc.) that causes traumatic erosion, ulcer, leukoplasia or leukokeratosis (keratinization of mucosa that later may lead to pernicious degeneration)
- Infection diseases affecting the mucosa as a result of penetration of viruses, microbes, fungi.
- More often the reasons of pathologic changes of mucosa are the disorders of different organ-systems in the organism: allergy, diseases of cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine, blood, skin, tuberculosis, AIDS, etc.
Sometimes to find the reason of mucosa pathology is rather difficult: in that case one needs great experience, high professionalism, ability not only to gather much information but also skills to render and make conclusions on it.
In ‘Aregak’ dental clinic the experienced doctor-dentists are able to diagnose the existing oral mucosa diseases of concrete patient; they find the reasons and accordingly prescribe appropriate treatment.
All inflammatory diseases of mucosa are called identically-stomatitis. If the pathologic process is on the tongue, it is called glossitis, if on the gingiva-gingivitis, if on the lips-cheilitis. When the mucosa starts thickening, calcifies and starts to peel then special type of the illness is existent-leukoplakia.
The common symptom of stomatitis is the appearance of niduses of reddening, acnes, erosions or ulcers, incrustation. Those niduses often appear on the buccal mucosa, on the oral cavity floor, palate, on the tip of the tongue. Sometimes enlargement of lymphatic nodes placed near the erosions and ulcers is detected, in other cases the body temperature raises. The average of duration of the illness is 7-14 days. Stomatitis may be repeated if the immunity is law, there are feeding disorders, hypovitaminosis, infection diseases; moreover, the exacerbations happen often in the spring and autumn.
The diagnosis of oral mucosa diseases is done by detailed clinical examination of the patient that allows the dentist to detect the degree of pathologic process and its prevalence, the reaction of the organism towards the inflammation. It is very important to find the real reason of the illness (trauma, infection, allergy, pathology of inner organs, hypovitaminosis, etc.) for the productivity of the treatment and the prevention of later exacerbation depend on it.
The etiotropic and pathogenic therapy set to eliminate the reasons of the diseases (in case of infection stomatitis, glossitis, chelitis-antibacterial, antivirus therapy, in case of hypovitaminosis-vitamin therapy, treatment of the main illness because of which the oral mucosa diseases generated).
Local therapy set to eliminate the local traumatic factors, the main symptoms of the disease and to recover quickly the existing erosions and ulcers.
General recovering therapy that stimulates the protective forces of the organism.
Turning to dentist in case of first symptoms of oral mucosa diseases is the guarantee of quick recovery.
Stomatitis is the general name given to the diseases of oral mucosa. The following pathology develops, as a rule, because of general and local reduction of immunity. According the causes of generation the following types of stomatitis are differentiated:
- Chronically repeated aphthous stomatitis
- Herpetic
- Ulcero-necrotic
- Oral moniliasis
Chronic aphthous stomatitis manifests itself either on the lips, on bucca, on palate or on the tongue mucosa in the form of sore aphthа. The main causative agents are microbes and viruses. The illness is generated when the balance of vitamins B1 and B12 in the organism is disturbed. It is often observed in case of chronic diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
The causative agent herpetic stomatitis is the ordinary herpes virus. Most often it occurs to children 1-3 years. In that case at the beginning of the disease the child has common symptoms of general intoxication:
- general malaise,
- high temperature,
- enlargement of lymphatic nodes,
- nausea and vomiting
- diarrhea.
Then on the oral mucosa and on the edges of the lips acnes appear in places of which erosions appear quickly with typical irregular edges. After nearly 8-10 days the illness is cured.
To ulcero-necrotic stomatitis the necrosis of gingiva is typical. The inflammation usually starts from inter-dental papillae and the mucosa surrounding, especially buccal mucosa. Then sore and easily bleeding ulcers appear that join quickly and form rather big ulcers of mucosa. As a result active necrotic lesion is started; there is odor of rotting in the mouth.
This kind of lesion is detected in case of insufficient oral hygiene especially to people of 17-30 years.
The ulcero-necrotic stomatitis may be accompanied by flu, quinsy, ARD, blood diseases, AIDS, tuberculosis, and raise rather unpleasant and serious complications. In case of such lesion of mucosa besides the rash symptoms of intoxication are also possible: high temperature, general malaise, enlargement of lymphatic nodes and pain.
Oral moniliasis is a rater widespread disease of oral mucosa the causative agent of which is the fungi called Candida. In this case there is dryness, burning in the mouth cavity; white incrustation is formed (while cleaning it the mucosa is bleeding).
In case of first symptoms of each kind of stomatitis it is necessary to turn to dentist. No self-treatment should be done. First the doctor will put diagnosis then he will start treatment. To prevent stomatitis one must keep always private oral hygiene and, of course, be attentive towards his own health.
Stomatitis depending on clinical manifestation may be catarrhal, ulcer and aphthous.
Catarrhal stomatitis is one of the most frequently accruing lesions. The reasons of its generation are the local factors-when the oral hygiene is not kept, the dental diseases, oral dysbacteriosis. The illnesses of gastrointestinal tract such as gastritis, duodenitis, colitis, helminthiasis can also cause stomatitis. In case of catarrhal stomatitis the oral mucosa swells, hyperemia is detected; it can be covered with white or yellow incrustation. Hypersalivatation is also detected. Gingiva bleeding and fetid odor in the mouth are also possible.
The treatment of catarrhal stomatitis is the elimination of local causes-cleaning of dental tartars, teeth healing. The mucosa is disinfected chlorhexidine liquor of 0.05 % and 0.1%. In a day one must polish the mouth cavity with tincture of chamomile, marigold and keep special diet. Generally after 5-10 days stomatitis is cured. But if the phenomena do not eliminate then the general reasons should be revealed that might be illnesses of gastrointestinal tract or helminthiasis. In this case local and general therapies are combined.
The ulcer stomatitis is a more severe disease than the catarrhal; it can either develop itself or be the complication of catarrhal stomatitis. The ulcer stomatitis is often generated to the people having stomach ulcer illness or chronic enteritis, as well as in case of cardiovascular, blood, infection diseases and intoxications. Unlike catarrhal stomatitis that infects the superficial layer of the mucosa, the ulcer stomatitis infects the whole mucosa.
The primary symptoms of catarrhal and ulcer stomatitis are similar, but later in case of ulcer stomatitis high temperature, malaise, headache, enlargement of lymphatic nodes and pain are detected. The patient feels strong pain while eating. These symptoms, of course, make the patient to turn to doctor.
Aphthous stomatitis shows itself by generating one or several aphthas on the oral mucosa. The aphthas are oval or round, in the size of lentil grain, with clear red lines with gray-yellow incrustation in the middle.
The gastrointestinal illnesses, allergic reactions, virus infections, rheumatism may cause aphthous stomatitis. The disease starts with general malaise, high temperature and pain in the mouth cavity in the places of aphthas. To treat this illness one must turn to doctor immediately.
Leukoplakia is the chronic lesion of oral mucosa which causes keratinization of epithelium (hyperkeratosis). It is detected generally to men older 40 years and is placed on the buccal mucosa, in the corners of mouth, in the lateral zones of the tongue.
The causes of leukoplakia might be the mechanical traumas of the mucosa from the retractors of dental prosthesis, from too hot or cold food and so on. This illness often does not have expressed symptoms, but the patient may have the feeling of light itching and burning. But the disease is dangerous as it can change into a pernicious degeneration, thus it is necessary to turn to a doctor-oncologist.
Glossitis is the inflammation of the tongue tissues. It can be both superficial and deep. More often glossitis is a symptom of some other illness of the organism, but it may be an independent disease as well.
The main reasons of the development of glossitis are dental caries, tartars, the traumas of tongue and mouth cavity, smoking, alcoholism, insufficient oral hygiene, the lesion with salts of hard metals, scalding, too hot food, hot spices, allergies and so on.
Superficial glossitis might be a symptom of gastrointestinal tract, infection diseases. It shows itself by incrustation, swell on the tongue, thickening and limitation of mobility. The tongue gets bright red color, feeling of burning on the tongue raises, it is painful, the taste feeling is lost and hypersalivation is detected.
The treatment of superficial glossitis is performed by local anesthesia and with antibacterial means. Multivitamin complexes, antihistamines are prescribed. Great role has the oral cavity sanation (the elaboration of the open wound with special materials and extraction of dead tissues, so that nothing would impede the rehabilitation).
In case of deep glossitis it is a bit difficult. The inflammatory lesion takes place in the tongue and an abscess is developed (pus accumulation that generates in case of acute or chronic infection nidus). The deep glossitis may spread over the floor of the mouth and generate inflammation in the zones of chin and isthmus. In this case a surgical treatment is indicated.
Besides the above mentioned there are also non-inflammatory types of glossitis, t. e. desquamative glossitis (geographical language).
This type of the illness is detected in case of pregnancy, gastrointestinal tract, blood illnesses, metabolic disorders, in case of some infection diseases, helminthiasis, rheumatism.
In case of desquamative glossitis the epithelium of the tongue surface and lateral parts is expressed by nidus. The alliteration of the niduses of epitheliums being decayed and restored makes the surface of the tongue look like a map. Besides external changes, there is also a feeling of burning and pain.
The treatment of desquamative glossitis is based on the treatment of the main disease because of which the glossitis is developed.
The glossitis may also be rhombus-like, which is an inborn anomaly; villiferous, which is described by enlargement and keratinization of filamentous papillae; folded, which is an inborn anomaly: on the tongue plaits appear, but is doesn’t cause complaints; atrophic, which is one of the symptoms of anemia which is generated because of the insufficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid, the tongue becomes bold without any papillae; interstitial, this type is developed in case of the syphilis, the tongue scleroses and its mobility is limited.
The prevention of glossitis demands sufficient oral and dental hygiene, regular visits to dentist, healthy food.
The treatment of oral mucosa diseases mainly is done by elimination of provocative reasons. Oral cavity sanation is done, the acute angles of teeth are flattened, the dental prosthesis is chosen correctly. The patient is prescribed healthy diet; the patient quits smoking and doesn’t eat too hot and spicy food.
To treat stomatitis the dental tartars are extracted and the ill teeth are treated. Antiseptic means are prescribed to polish oral cavity, the tincture of chamomile and marigold among them. If the stomatitis is not recovered in 5-10 days it means there is gastrointestinal tract disease or helminthiasis. In this case the general therapy course is chosen.
In ‘Aregak’ dental clinic diagnosis and treatment of oral mucosa diseases are done. These illnesses are quite diverse and often make the patient suffer. For that reason they should be diagnosed and treated on time. Besides the diagnosis of oral mucosa diseases would allow to determine the state of inner organs which is very important as it does not demand laboratorial methods.
Teeth Restoration
Teeth restoration is one branches of modern stomatology that allows to restore the anatomic form, structure, enamel color of the injured teeth, as well as to eliminate inborn and acquired defects of the denture.
Aesthetic dentistry first of all is the esthetic restoration to teeth after which the patient gets a beautiful smile without prosthetics.
In the esthetic stomatology three interconnected concepts are distinguished-teeth restoration, construction, transformation. In the aesthetic dentistry there are various methods that allow the patient to get a fantastically beautiful smile.
- caries,
- tooth splitting,
- pathologic abrasion,
- stains on the frontal teeth,
- cuneiform defects, erosion, fluorosis
Teeth restoration allows restoring the form of tooth and denture, change the color of tooth, to close the fissures between teeth.
In the aesthetic restorative technology 2 groups of materials are used-composites and compomers. The compomers are restorative lighto-solidificated materials of the new generation that enforces the dental tissue with fluorine preventing the caries generation around the filling. The modern materials have rather rich colorings which allow choosing the color of restored tooth precisely. As a result the right similarity of firm natural enamel is got. During the aesthetic restoration the physicians can also correct the form of the tooth.
The final restorative stage of the tooth is the abrasion and polishing.
The tooth restoration may be done during one visit to the dentist and return the shining smile due to the talent and skills of the doctor.
Today the modern dentistry offers a complete complex of aesthetic dental service to get beautiful and healthy teeth.
It includes:
- creation of even denture by changing their form,
- elimination of splitting,
- elimination of old inlay that has already changed its color
- elimination of small or big fissures between
- professional whitening
The aesthetic restoration may be done during one visit without making dental impression copying by restoring the dental crown layer by layer.
The other method of restoration is more laborious. First impression copying is done then in the laboratory the ceramic crown of the tooth is made. During this period the patient wares plastic crown. The next stage supposes the fixation of the crown with cement.
In such cases when the dental splits are rather big, or the caries cavity is big and it is impossible to restore the tooth with composite materials, method of orthopedic prosthesis is used. In this case are used
- ceramic inlays
- veneers and lumineers
- dental crowns (metal-ceramic, without metal, zircon)
Unlike micro-prosthetics and dental stopping, with the help of aesthetic restoration technique it is possible to change the color of frontal teeth, make the denture beautiful. The frontal teeth look fascinating while smiling, that’s why the aesthetic look is not less important than the functional.
If it is necessary to restore frontal teeth that have small defects then veneers are used to restore, if the defects are bigger then dental crowns without metal or zircon are used that have no metal base and are more esthetic.
The metal-ceramic inlays are used generally for restoring molars.
The veneers are ultrafine layers that are used with composite materials. With the help of veneers it is possible to hide splitting and cracks, to minimize the fissures between teeth, to cover the darkened tooth, stain on the tooth that is impossible to eliminate another way.
Another method of tooth restoration is post insertion. It is placed in the root and serves as a basis for crown. Most often metal or fiberglass posts are used.
The fiberglass posts do not affect the tooth color as far s they are white or transparent.
The next method of tooth restoration is the cosmetic restoration. This is a separate branch of aesthetic dentistry the aim of which is to correct the forms and the sizes of tooth. This method of restoration needs higher professionalism and higher aesthetic taste. The cosmetic restoration considers being an alternative variant for long orthopedic treatment. Sometimes it is preferable as it is not so expensive and the result is predictable and resistant.
The cosmetic restoration includes reconstruction of teeth, denture reconstruction and transformation with the help of which the form of teeth is corrected.
In the cosmetic dentistry for the same reasons teeth whitening procedure is performed. Principally this procedure has a cosmetic nature, it is not a medical procedure.